Governance
IT Security:
Computer security, also known as cyber security or IT security, is the protection of computer systems from the theft or damage to the hardware, software or the information on them, as well as from disruption or misdirection of the services they provide.
A vulnerability is a system susceptibility or flaw. Many vulnerabilities are documented in the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) database. An exploitable vulnerability is one for which at least one working attack or “exploit” exists.
To secure a computer system, it is important to understand the attacks.Computer security is critical in almost any industry which uses computers. Currently, most electronic devices such as computers, laptops and cellphones come with built in firewall security software, but despite this, computers are not 100 percent accurate and dependable to protect our data (Smith, Grabosky & Urbas, 2004.) There are many different ways of hacking into computers. It can be done through a network system, clicking into unknown links, connecting to unfamiliar Wi-Fi, downloading software and files from unsafe sites, power consumption, electromagnetic radiation waves, and many more. However, computers can be protected through well built software and hardware. By having strong internal interactions of properties, software complexity can prevent software crash and security failure.
IT Audit:
An IT audit is the examination and evaluation of an organization’s information technology infrastructure, policies and operations. Information technology audits determine whether IT controls protect corporate assets, ensure data integrity and are aligned with the business’s overall goals.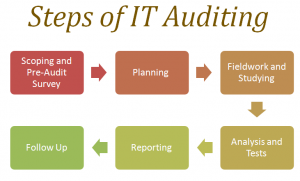
IT auditors examine not only physical security controls, but also overall business and financial controls that involve information technology systems.
Because operations at modern companies are increasingly computerized, IT audits are used to ensure information-related controls and processes are working properly. The primary objectives of an IT audit include:
- Evaluate the systems and processes in place that secure company data.
- Determine risks to a company’s information assets, and help identify methods to minimize those risks.
- Ensure information management processes are in compliance with IT-specific laws, policies and standards.
- Determine inefficiencies in IT systems and associated management.
PMO Training’s:
The Project Management Office (PMO) is one of the fastest emerging organizational structures across all industries. The courses offered by PMO Advisory focus on the challenges that are important to effectively manage intense project environments and explore the best practices to improve communication, cut costs and optimize resource utilization. Our courses provide strategies and tactics to enable process improvement for a currently established Project Management Office.
- Gaining an indepth understanding of the services a well designed PMO should perform for the organization
- Understanding the challenges the PMO faces within their organization, and how to address them
- Learning how to evaluate key metrics of success for the PMO, and how to improve PMO performance
- Learning techniques to manage project portfolios more effectively
- Improving on risk management strategies and tactics for addressing risk
- Learning how leading companies operate their project management offices (PMOs), and which of their strategies and tactics may be right for their organization

