Cloud Services
A cloud service is any service made available to users on demand via the Internet from a cloud computing provider’s servers as opposed to being provided from a company’s own on-premises servers.
Cloud services are designed to provide easy, scalable access to applications, resources and services, and are fully managed by a cloud services provider.A cloud service can dynamically scale to meet the needs of its users, and because the service provider supplies the hardware and software necessary for the service,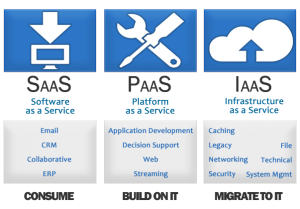 there’s no need for a company to provision or deploy its own resources or allocate IT staff to manage the service. Examples of cloud services include online data storage and backup solutions, Web-based e-mail services, hosted office suites and document collaboration services, database processing, managed technical support services and more.
there’s no need for a company to provision or deploy its own resources or allocate IT staff to manage the service. Examples of cloud services include online data storage and backup solutions, Web-based e-mail services, hosted office suites and document collaboration services, database processing, managed technical support services and more.
Although cloud computing has changed over time, it has been divided into three broad service categories: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and software as a service (SaaS).
Security remains a primary concern for businesses contemplating cloud adoption — especially public cloud adoption. Public cloud providers share their underlying hardware infrastructure between numerous customers, as public cloud is a multi-tenant environment. This environment demands copious isolation between logical compute resources. At the same time, access to public cloud storage and compute resources is guarded by account logon credentials.
Private cloud services are delivered from a business’ data center to internal users. This model offers versatility and convenience, while preserving the management, control and security common to local data centers. Internal users may or may not be billed for services through IT chargeback.
In the public cloud model, a third-party provider delivers the cloud service over the internet. Public cloud services are sold on demand, typically by the minute or hour. Customers only pay for the CPU cycles, storage or bandwidth they consume. Leading public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, IBM SoftLayer and Google Compute Engine.
typically by the minute or hour. Customers only pay for the CPU cycles, storage or bandwidth they consume. Leading public cloud providers include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, IBM SoftLayer and Google Compute Engine.
Hybrid cloud is a combination of public cloud services and on-premises private cloud — with orchestration and automation between the two. Companies can run mission-critical workloads or sensitive applications on the private cloud while using the public cloud for bursting workloads that must scale on demand. The goal of hybrid cloud is to create a unified, automated, scalable environment that takes advantage of all that a public cloud infrastructure can provide while still maintaining control over mission-critical data.

